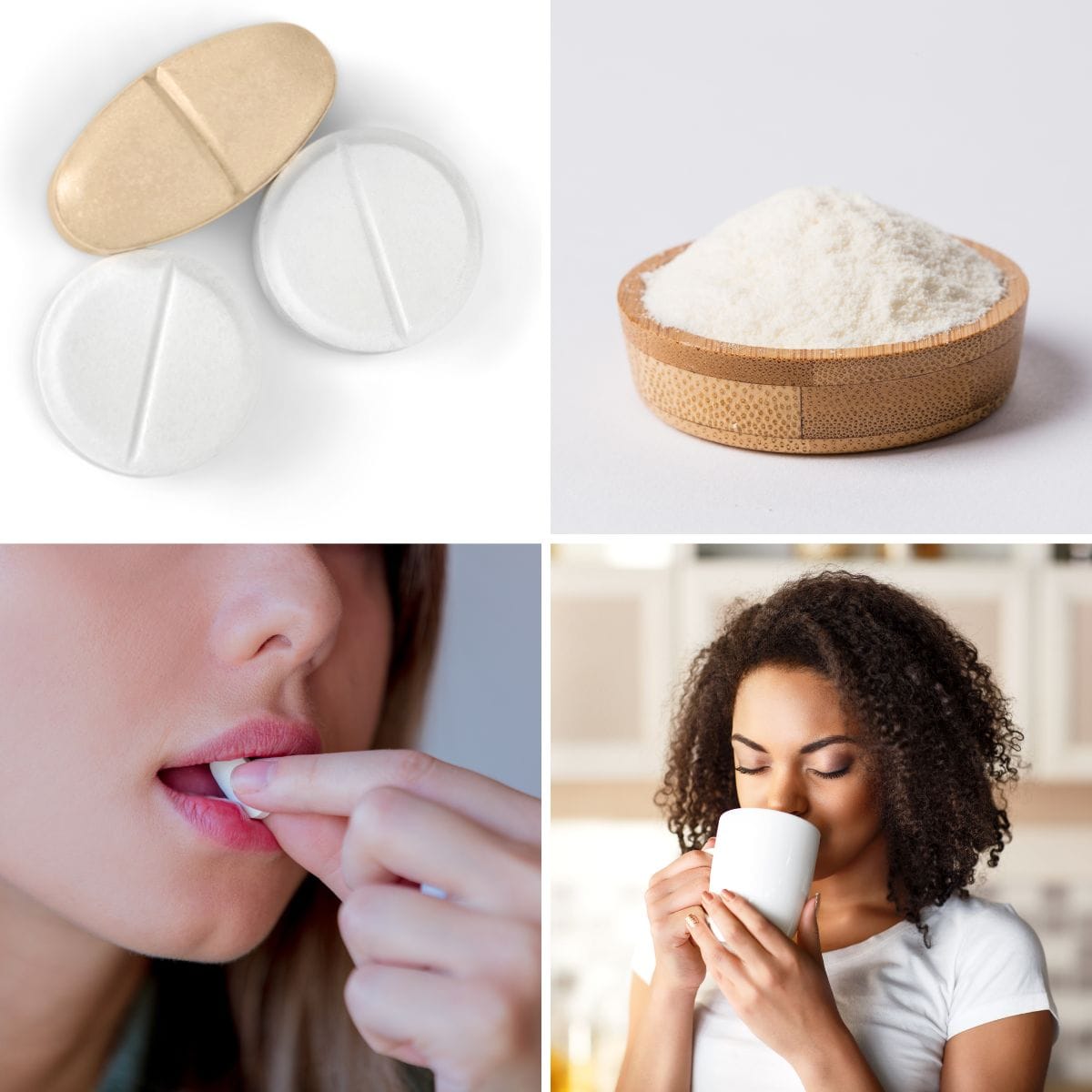
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the differences between probiotic powders and tablets can help you make an informed decision for your digestive health.
- The effectiveness of probiotics depends on the survival of the bacteria through the stomach acid to the intestines.
- Both forms have their unique advantages and considerations, including convenience, dosage, and the presence of other nutrients.
Probiotics have become a staple in the pursuit of good gut health, with a myriad of products flooding the market. Among the plethora of options, consumers often find themselves pondering, "Is it better to take probiotics in powder or tablet form?" This article aims to dissect the pros and cons of each, helping you make an educated choice for your overall health.
The Battle of Forms: Powders vs. Tablets
When it comes to probiotic supplements, the form can significantly influence the survival rates of the beneficial bacteria they contain. Probiotic powders offer more room for a higher number of bacterial strains and potentially a higher dose of live microorganisms. On the other hand, probiotic capsules or tablets are often designed with delayed release properties to protect the microbes from hydrochloric acid in the stomach, ensuring more bacteria reach the small intestine alive.
Survival Through Stomach Acid
A critical factor in the effectiveness of probiotic supplements is their ability to withstand the harsh environment of the stomach. The acidic conditions are detrimental to many probiotic strains. Powdered probiotics can be mixed with liquids or food sources, which may buffer the stomach acid and protect the bacteria inside. Tablets, especially those with delayed release capsules, are engineered to bypass the stomach's hydrochloric acid, releasing the good bacteria directly into the intestines where they are needed.
Dosage and Potency
Determining the right dose of probiotics is essential for reaping their potential health benefits. Powdered forms often allow for adjustable dosages, making it easier to increase or decrease the amount of beneficial microorganisms you consume. Tablets, however, provide a precise, pre-measured dose, which can be convenient for those who prefer not to measure out their supplements.
The Shelf Life Dilemma
Probiotics, being live organisms, have a shorter shelf life compared to other nutrients. Probiotic powders may lose potency faster once opened, as they are exposed to air and moisture. Tablets, in contrast, are typically sealed in individual blister packs or bottles with moisture-absorbing packets, which can extend their viability.
Customization and Flexibility
When considering a probiotic supplement, customization and flexibility often play a pivotal role in user preference. Probiotic powders offer a distinct advantage in this regard. They can be easily adjusted in terms of dosage, allowing individuals to tailor their intake to their specific needs. For instance, someone just starting with probiotics might prefer a smaller dose to ease their digestive system into it, which is more manageable in powder form.
Moreover, probiotic powders are versatile in their use. They can be mixed into a variety of foods and beverages, from smoothies to yogurt, without altering the taste significantly. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for those who have difficulty swallowing pills or for children who might be averse to taking medicine in capsule form. The ability to mix probiotic powder into a preferred food or drink makes it a convenient option for many.
Cost-Effectiveness of Probiotic Forms
When considering probiotics, the cost is a significant factor for many consumers. Probiotic powders often present a more budget-friendly option compared to tablets. This is partly because powders require fewer manufacturing steps and don't need the binders and fillers that tablets do. As a result, you might get more probiotic bang for your buck with powders, especially if you're on a tight budget or looking to incorporate these beneficial bacteria into your daily routine without breaking the bank.
However, it's important to note that while powders may be more cost-effective upfront, the longevity of probiotics can be compromised if not stored correctly. Probiotics die off faster when exposed to heat, moisture, and light, and powders can be particularly susceptible to these elements once opened. Tablets, on the other hand, typically have a longer shelf life and may retain their potency over time, potentially offering better value in the long run despite a higher initial cost.
Incorporating Probiotics into Your Diet
For those looking to boost their intake of probiotics, fermented tea, such as kombucha, is a popular choice. This effervescent fermented tea is not only rich in probiotics but also offers a unique flavor that many enjoy as part of their daily routine. Kombucha can be a delightful way to introduce beneficial bacteria into your diet, and it comes with the added benefits of tea's antioxidants. However, the probiotic content in kombucha can vary widely depending on the brand and brewing time, so it's worth doing some research to find the most beneficial option.
In contrast, for individuals who prefer a more controlled and measured approach to their probiotic intake, supplements in powder or tablet form may be preferable. These forms ensure a specific dose of probiotics, which can be particularly important for those using them to address specific health issues. It's crucial to remember that probiotics die off over time, so whether you choose fermented tea or a supplement, check the expiration date and storage instructions to ensure you're getting the live cultures your gut needs.
Probiotic Foods vs. Supplements
While discussing probiotic bacteria, it's essential to differentiate between probiotic foods and supplements. Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kombucha are natural sources of probiotics. These foods not only provide a rich array of probiotic strains but also come with additional nutrients that can benefit the intestinal tract. For healthy people, incorporating fermented foods into their diet is an excellent way to support their digestive system.
On the other hand, probiotic supplements, whether in powder or tablet form, offer a more concentrated dose of probiotics. They are particularly useful for individuals who may not consume enough probiotic foods in their diet or have specific health conditions that require targeted strains of probiotic bacteria. Supplements ensure a consistent and measurable intake of probiotics, which can be crucial for restoring the balance of the intestinal tract after an illness or antibiotic treatment.
Additional Nutrients and Prebiotics
Some probiotic supplements come fortified with additional vitamins or prebiotics, which are non-digestible fibers that feed the good bacteria. Powdered probiotics often have more room to include these extra health-promoting ingredients. Tablets may also contain them, but the form factor can limit the amount that can be added without increasing the pill size.
Ease of Consumption
For some, the ease of swallowing a tablet outweighs the flexibility of powders. Tablets are convenient, portable, and don't require preparation. Probiotic powders, however, can be mixed into a variety of foods and beverages, like yogurt or kefir, which are already rich in live bacteria and other nutrients, enhancing the probiotic intake.
Considerations for Specific Health Conditions
Individuals with health problems such as irritable bowel syndrome or a compromised immune system may require specific bacterial strains or higher doses of probiotics. Consulting with a doctor can provide guidance on whether probiotic powders or tablets are more suitable for these conditions, considering factors like the form's ability to deliver live bacteria effectively to the gastrointestinal tract.
Research and Evidence
Scientific research continues to explore the benefits of probiotics for digestive health and beyond. Studies often use different forms of probiotics, and it's important to consider the evidence supporting the efficacy of powder or tablet forms for conditions like high blood pressure, digestion issues, or maintaining a balance of good and bad bacteria.
Summary
Choosing between probiotic powders and tablets boils down to personal preference, lifestyle, and specific health needs. Powders offer flexibility in dosage and can be combined with fermented foods for added benefits, while tablets provide convenience and potentially better protection against stomach acid. Both forms aim to support good gut health, but it's crucial to select a product based on quality, viability of the probiotic strains, and your body's unique requirements.
FAQ Section
Q: Can I take probiotic supplements with other medications? A: Generally, probiotics can be taken alongside other medications, but it's always best to consult with your doctor, as certain medicines may interact with probiotics.
Q: How do I know if I need to take probiotics? A: If you're experiencing digestive issues, have been on antibiotics, or want to support your overall health, probiotics may be beneficial. However, it's important to talk to a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Q: Should probiotics be taken with food or on an empty stomach? A: This can depend on the form and brand of the probiotic. Some are designed to be taken with meals to buffer the stomach acid, while others are best taken on an empty stomach. Always follow the instructions on the supplement label or consult your doctor.