Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the benefits and timing of magnesium and potassium supplementation can enhance overall health.
- Nighttime supplementation may offer specific advantages for sleep quality and muscle relaxation.
- Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential before starting any supplement regimen.
Magnesium and potassium are two essential minerals that play crucial roles in maintaining various bodily functions. From muscle contractions and nerve function to heart health and fluid balance, these minerals are vital for a healthy lifestyle. But when it comes to supplementation, timing can be everything. In this article, we'll explore whether taking magnesium and potassium at night could be beneficial for your health.
The Role of Magnesium in the Body
Magnesium is a powerhouse mineral involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the human body. It contributes to bone health, helps regulate muscle and nerve function, and is essential for energy production. A magnesium deficiency can lead to a host of health issues, including muscle cramps, mental fatigue, and irregular heart rhythms.
Potassium's Importance for Health
Potassium acts as an electrolyte, helping to maintain extracellular potassium homeostasis and regulate fluid balance within the body. It's also critical for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels and proper function of the heart muscle and nerve cells. Low potassium levels can result in weakness, fatigue, and in severe cases, cardiac arrhythmias.
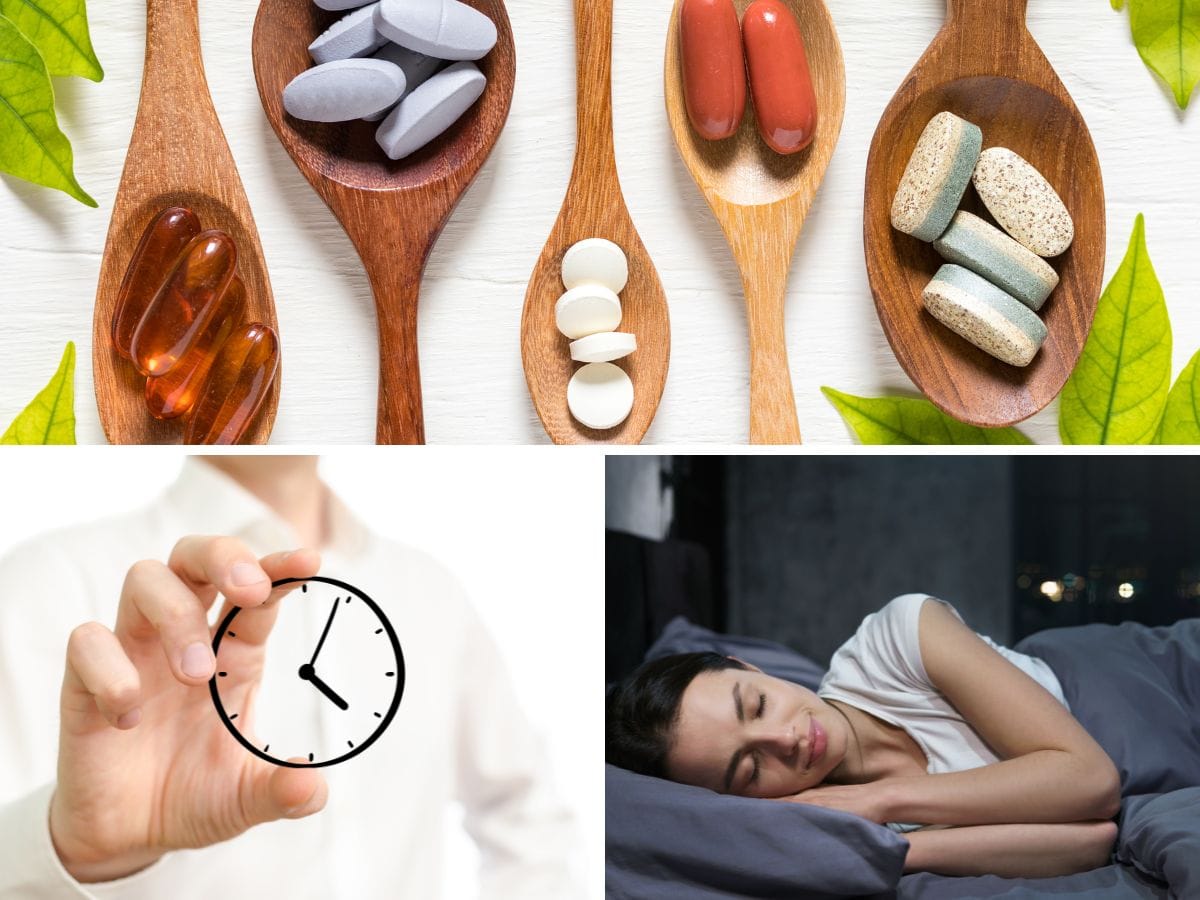
Benefits of Taking Supplements at Night
Taking magnesium and potassium supplements at night may have specific benefits. Magnesium, for instance, is known for its ability to support relaxation and may help improve sleep quality. Potassium supplementation at night can aid in muscle relaxation and prevent nocturnal leg cramps, a common disturbance that can interrupt sleep.
Understanding Magnesium Supplements
Magnesium supplements come in various forms, including magnesium citrate, magnesium oxide, magnesium glycinate, and magnesium gluconate. Each form has different absorption rates and uses. For example, magnesium citrate is often used for its laxative effect, while magnesium glycinate is preferred for its calming properties.
Potassium Supplement Forms
Potassium supplements are available as potassium chloride, potassium citrate, and salt substitutes that contain potassium. It's important to choose the right supplement form to match your health needs. Potassium chloride is commonly used to treat low potassium levels, while potassium citrate can help prevent kidney stones.
The Synergy of Magnesium and Potassium
Both magnesium and potassium work together to support muscle and nerve function. Magnesium helps the body utilize potassium effectively, which is why a combined intake of these minerals can be particularly beneficial. This synergy can contribute to better muscle function, heart health, and nerve signaling.
Dietary Sources of Magnesium and Potassium
While supplements can help, obtaining these minerals through a balanced diet is crucial. Magnesium-rich foods include dark leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Potassium-rich foods encompass green leafy vegetables, bananas, oranges, and soy milk. A diet rich in these foods can help maintain an adequate intake of both minerals.
Optimizing Your Intake: Timing and Dosage
When considering potassium and magnesium supplements, it's not just about whether to take them, but also about when and how much. For optimal health, the timing of your supplementation can be as crucial as the dosage. Magnesium supplementation, for instance, is often recommended in the evening, as it may aid in muscle relaxation and improve sleep quality. However, it's essential to follow the recommended daily allowances or a healthcare provider's advice to avoid overconsumption, which can lead to adverse effects.
Potassium, on the other hand, plays a pivotal role in maintaining serum magnesium levels and ensuring proper muscle contraction. While dietary potassium is abundant in certain foods like cooked spinach and bananas, supplements can help fill the gap in case of a potassium deficiency. It's important to balance your sodium intake with adequate amounts of potassium to maintain blood pressure within a healthy range. Most supplements will provide guidelines, but consulting with a healthcare professional can tailor the dosage to your individual needs.
The Interplay Between Diet and Supplementation
The relationship between dietary choices and the need for dietary supplements is a nuanced one. Processed foods often lack essential minerals, leading to deficiencies that might necessitate magnesium supplementation. The body's magnesium is primarily stored in the bones and soft tissues, and a regular diet may not always provide adequate amounts. Including magnesium and potassium-rich foods in your diet, such as nuts, seeds, and leafy greens, can complement supplementation efforts for a holistic approach to mineral intake.
Conversely, too much reliance on supplements can sometimes lead to neglecting the rich variety of potassium ions available in a balanced diet. Potassium-rich foods not only contribute to keeping high blood pressure at bay but also support the production of red blood cells and overall immune health. While hypokalemic periodic paralysis is a rare condition, it underscores the importance of maintaining proper potassium levels, which can often be achieved through a combination of dietary mindfulness and supplementation.
When to Consider Supplementation
Supplementation may be necessary when dietary intake is insufficient or when certain health conditions require increased potassium intake or more magnesium. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen, as high doses can have adverse effects.
The Impact on Blood Pressure and Heart Health
Magnesium and potassium both play a role in maintaining optimal blood pressure and heart health. Adequate levels of these minerals can help prevent hypertension and support the heart muscle. Taking supplements at night may also aid in reducing the risk of nocturnal hypertension, a condition where blood pressure spikes during sleep.
Muscle and Nerve Health
Magnesium and potassium are crucial for proper muscle contractions and nerve signal transmission. A deficiency in either mineral can lead to muscle weakness and cramps. Supplementing at night can help ensure these minerals are available when the body is in repair mode during sleep.
Mental Health and Sleep Quality
Magnesium has been linked to improved mental health and reduced anxiety, which can promote better sleep. Potassium also contributes to mental well-being by supporting the function of neurotransmitters. Taking these supplements at night might enhance the quality of sleep and support mental health.
Kidney Function and Fluid Balance
Both minerals are essential for kidney function and maintaining fluid balance in the body. Adequate levels of magnesium and potassium help the kidneys filter waste efficiently and regulate the body's water content. Nighttime supplementation can support these processes during the body's natural detoxification cycle.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
While magnesium and potassium supplements are generally safe, they can cause side effects like gastrointestinal discomfort or affect the absorption of other medications. It's important to be aware of these potential interactions and to follow the recommended intake guidelines.
How to Choose the Right Supplement
Selecting the right supplement form and dose is crucial for safety and effectiveness. Factors such as existing health conditions, dietary restrictions, and individual mineral levels should be considered. A healthcare provider can help determine the most appropriate supplement form and standard dose for your needs.
Summary
Magnesium and potassium are important minerals that support numerous bodily functions, including heart health, muscle function, and nerve signaling. Taking magnesium and potassium at night may offer benefits such as improved sleep quality, muscle relaxation, and better absorption. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before beginning any supplementation to ensure it's safe and appropriate for your individual health needs.
FAQ Section
Q: Can taking magnesium and potassium at night improve sleep? A: Yes, magnesium is known for its relaxation properties and may improve sleep quality. Potassium can also aid in muscle relaxation, potentially leading to better sleep.
Q: Are there any risks associated with taking magnesium and potassium supplements at night? A: While generally safe, taking high doses or incorrect forms of these supplements can lead to side effects or interact with other medications. It's important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting supplementation.
Q: How do I know if I need magnesium and potassium supplements? A: If you're experiencing symptoms of deficiency, such as muscle cramps, fatigue, or irregular heartbeats, or if you have a medical condition that affects mineral absorption, you might benefit from supplementation. A healthcare provider can provide a proper assessment and recommendation.