Key Takeaways:
- Chelated magnesium is known for its superior bioavailability and is essential for numerous bodily functions.
- It can help in improving muscle and nerve function, sleep quality, and maintaining a healthy immune system.
- Understanding the different forms of magnesium and their absorption can guide you in choosing the right supplement for your needs.
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a pivotal role in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the human body. It's crucial for energy production, muscle function, nerve function, and maintaining a healthy immune system. However, not all forms of magnesium are created equal. This is where chelated magnesium comes into play. But what does chelated magnesium do, and how does it differ from other forms like magnesium oxide or magnesium citrate?
Understanding Chelated Magnesium
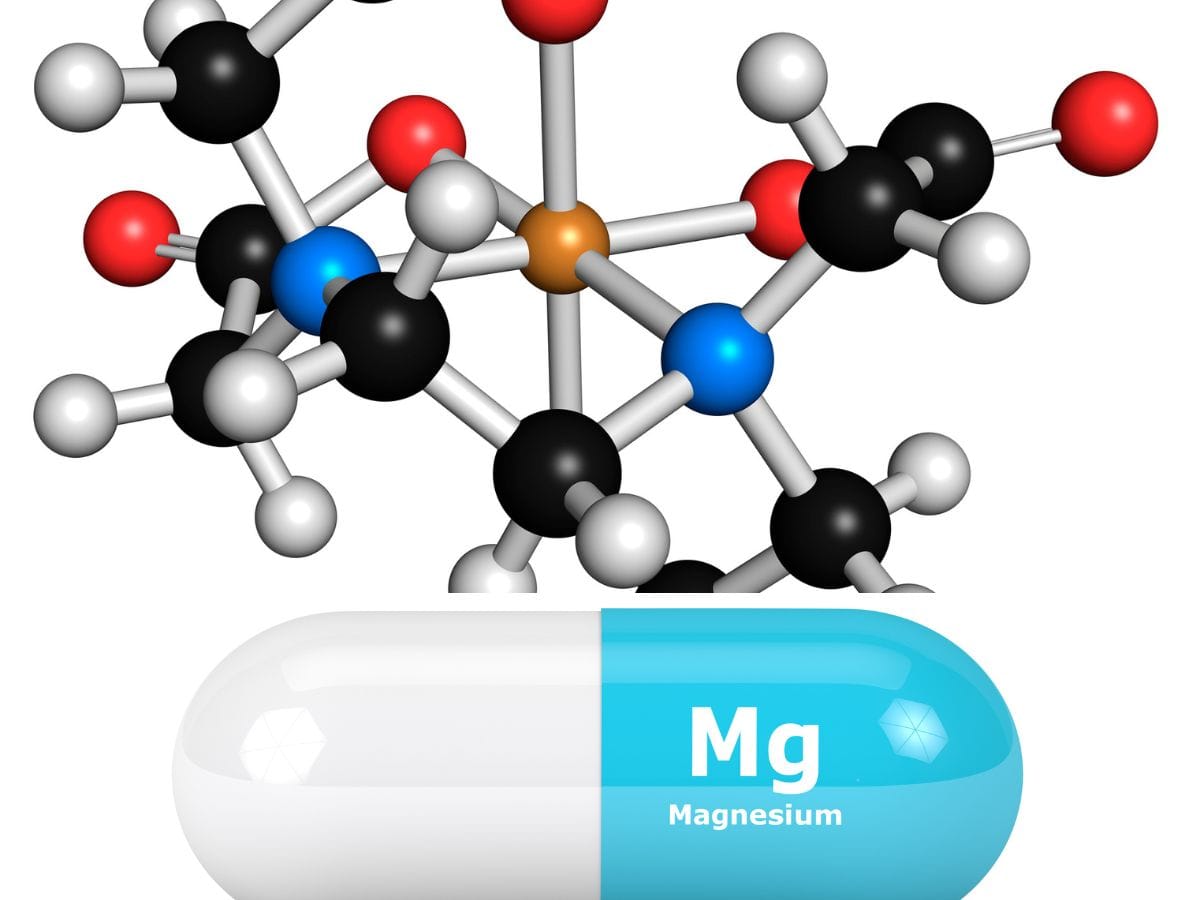
Chelated magnesium refers to magnesium that is bound to organic compounds, typically an amino acid, to enhance its absorption in the digestive system. The term "chelated" is derived from the Greek word "chele," which means claw, indicating how the mineral is held by the chelating agents. This form of magnesium is believed to have higher bioavailability, meaning the body absorbs it more efficiently than non-chelated forms.
The Chelation Process and Its Benefits
The chelation process involves attaching magnesium to amino acids, such as the amino acid glycine, to form magnesium glycinate, or to citric acid, creating magnesium citrate. These chelated forms of magnesium are designed to pass through the gastrointestinal tract more easily, leading to better bioavailability and fewer digestive issues like abdominal cramping or upset stomach that are often associated with other magnesium forms.
Magnesium Glycinate: A Popular Chelate
Magnesium glycinate, also known as magnesium bisglycinate, is a commonly used chelated form of magnesium. It combines magnesium with the amino acid glycine, which is known for its calming effects on the brain. This makes magnesium glycinate an excellent choice for those looking to improve sleep quality or manage stress.
The Role of Magnesium in Muscle and Nerve Function
Magnesium plays a critical role in muscle contraction and relaxation. It also supports nerve function by regulating neurotransmitters, which send messages throughout the brain and nervous system. Taking chelated magnesium can help alleviate muscle weakness and support overall nerve health.
Boosting Heart Health with Chelated Magnesium
Magnesium is vital for heart health, as it helps regulate blood pressure and supports the heart muscle's normal rhythm. Chelated magnesium supplements, due to their superior bioavailability, may be more effective in supporting cardiovascular health compared to other forms of magnesium.
Chelated Magnesium and Bone Health
Magnesium is essential for bone formation and influences the activities of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone health. It also impacts the concentration of parathyroid hormone and the active form of vitamin D, which are crucial for bone health. Chelated magnesium, with its enhanced absorption, can contribute to maintaining strong bones.
Magnesium and Digestive Health
Individuals with conditions like inflammatory bowel disease may have difficulty absorbing magnesium. Chelated magnesium helps by being more easily absorbed, thus potentially benefiting those with compromised digestive systems.
Magnesium Supplementation and Sleep Quality
Magnesium has a natural calming effect on the nervous system, making it a go-to mineral for improving sleep. Chelated magnesium, particularly magnesium glycinate, is often recommended for its ability to improve sleep quality due to its calming properties.
Magnesium Chelates and Mental Health
The term "chelated" refers to the bonding of magnesium to other molecules, which enhances its absorption and bioavailability. This is particularly important when considering the role of magnesium in mental health. Studies have shown that a chelated magnesium supplement can have a positive impact on mood and cognitive function. Magnesium plays a crucial role in neurotransmitter release and can help manage stress and anxiety, making it a vital mineral for maintaining mental well-being.
Moreover, magnesium chelates are often recommended over non-chelated magnesium due to their superior absorption rates. This means that the body can utilize more magnesium efficiently, which is essential for brain health. Adequate magnesium levels are associated with a lower risk of depression and have been used as an adjunct treatment for various mental health conditions. Including more magnesium-rich foods in one's diet, alongside a high-quality supplement formulation, can provide a solid foundation for mental health maintenance.
Magnesium Absorption: Chelated vs. Non-Chelated Forms
When discussing magnesium supplements, the term "chelated" refers to the bonding of magnesium ions to compounds that facilitate its absorption in the body. This is in contrast to non-chelated magnesium, which includes forms like magnesium oxide or magnesium sulfate. These non-chelated forms are often less expensive but also typically have lower bioavailability, meaning the body may not absorb them as efficiently. This can be particularly important for individuals who require magnesium supplementation for health reasons, as the effectiveness of the supplement is directly tied to its absorption rate.
In contrast, chelated magnesium is designed to pass more easily through the intestinal walls, making it more readily available for use by the body. This is because the chelation process protects the magnesium until it reaches the part of the gut where it's most easily absorbed. For those looking to increase their magnesium intake, understanding the differences between chelated and non-chelated forms is crucial. While chelated versions might come at a higher cost, their enhanced absorption capabilities can provide better value for those in need of magnesium supplementation.
Incorporating More Magnesium-Rich Foods into Your Diet
To complement magnesium supplementation, incorporating more magnesium-rich foods into your diet is a natural and effective strategy. Certain foods are known to be high in magnesium, including leafy greens like spinach and Swiss chard, nuts and seeds, legumes, whole grains, and dark chocolate. By increasing the intake of these foods, individuals can boost their magnesium levels through diet, which is often considered the most beneficial way to obtain essential nutrients. This approach also provides additional health benefits associated with a balanced and varied diet.
However, it's important to note that while these foods are beneficial, the magnesium they contain is in non-chelated form. This means that factors such as dietary fiber, phytic acid, and certain medications can interfere with how much magnesium is absorbed by the body. Despite this, a diet rich in magnesium-containing foods can significantly contribute to the overall magnesium intake and should be a part of a comprehensive approach to maintaining optimal magnesium levels, alongside considering mg preparations in supplement form if necessary.
The Synergy of Chelated Minerals in Supplement Formulation
When it comes to supplement formulation, the synergy between chelated minerals can significantly enhance overall efficacy. Chelated magnesium supplement products often include other chelated minerals like zinc, calcium, and iron, which work together to support various bodily functions. For instance, magnesium is known to aid in the absorption of calcium, which is vital for bone health, while zinc plays a critical role in immune function and wound healing.
In contrast, non-chelated forms of these minerals may compete for absorption, leading to less effective uptake and potential deficiencies. By choosing a supplement that combines chelated minerals, individuals can ensure they are getting the most out of their supplementation. This is particularly important for those at risk of conditions like cardiovascular disease, where the balance of certain minerals is crucial. Including a variety of chelated minerals in supplement formulations is a strategic approach to enhancing overall health and preventing nutrient imbalances.
Addressing Subclinical Magnesium Deficiency
Many people may have a subclinical magnesium deficiency without realizing it, often due to a poor diet or increased magnesium needs. Chelated magnesium supplements can help address this deficiency more effectively than non-chelated magnesium due to their optimal absorption.
Magnesium Intake Through Diet
While supplements are beneficial, incorporating more magnesium-rich foods into your diet is also important. Foods like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains are excellent sources of magnesium. However, for those who struggle to get enough magnesium from their diet, chelated magnesium supplements can be a valuable addition.
Choosing the Right Magnesium Supplement
With various magnesium preparations available, such as magnesium chloride, magnesium stearate, and mg citrate found in different supplements, it's essential to choose a form with better bioavailability. Chelated magnesium supplements, like magnesium amino acid chelate or magnesium bisglycinate, are often recommended for their higher absorption rates.
Testing Bioavailability: Clinical Healthcare Insights
Clinical healthcare studies often test the bioavailability of different magnesium supplements. Chelated forms consistently show superior absorption and reduced urinary excretion, indicating that more of the mineral is retained for the body's use.
Magnesium and Its Co-Factors
When taking chelated magnesium, it's also important to consider other minerals and vitamins that work in synergy with magnesium, such as vitamin D, calcium, and potassium. Ensuring a balanced intake of these co-factors can enhance the benefits of magnesium supplementation.
The Impact of Magnesium on the Immune System
A healthy immune system relies on adequate magnesium levels. Chelated magnesium helps support immune function by participating in various immune processes and reducing inflammation, which is crucial for preventing illnesses.
Magnesium's Role in Energy Production
Magnesium is a key player in the production of ATP, the energy currency of the cell. By taking chelated magnesium, you can support your body's energy production, leading to improved overall vitality and well-being.
How to Take Chelated Magnesium
Chelated magnesium supplements are best taken in divided doses throughout the day to maximize absorption. It's also advisable to take them with meals to reduce the risk of an upset stomach and to further enhance intestinal absorption.
Summary
Chelated magnesium is a form of magnesium that is bound to amino acids or organic compounds to improve its absorption and effectiveness in the body. It supports muscle and nerve function, heart health, bone health, digestive health, and sleep quality. Chelated magnesium supplements, such as magnesium glycinate, are often recommended for their superior bioavailability and are particularly beneficial for those with a subclinical magnesium deficiency or those who need more magnesium due to a poor diet or health conditions. Choosing the right supplement and considering dietary sources of magnesium can help ensure optimal magnesium intake for overall health.
FAQ Section
Q: What does chelated magnesium do? A: Chelated magnesium provides a form of magnesium that is more easily absorbed by the body. It supports various bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function, heart health, bone health, and a healthy immune system. It also helps improve sleep quality and energy production.
Q: How does chelated magnesium differ from other forms of magnesium? A: Chelated magnesium is bound to amino acids or organic compounds, which enhances its absorption in the digestive system. This results in higher bioavailability and fewer digestive side effects compared to non-chelated forms like magnesium oxide or magnesium chloride.
Q: How should I take chelated magnesium supplements? A: Chelated magnesium supplements should be taken in divided doses throughout the day, preferably with meals, to maximize absorption and minimize any potential digestive discomfort. It's also important to consider the co-factors that work in synergy with magnesium, such as vitamin D, calcium, and potassium.